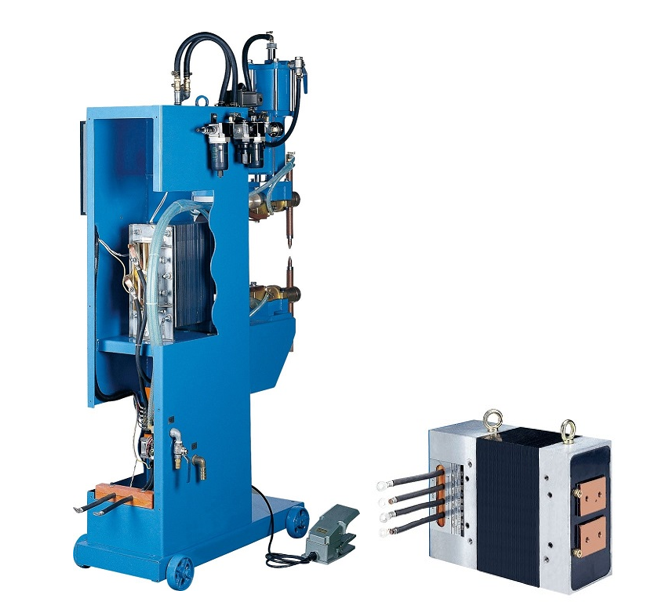
What is a welding transformer?
A resistance welding transformer is a transformer specifically designed for resistance welding. It reduces the voltage of the mains electricity but generates a high current of thousands to tens of thousands of amperes. This uses the resistance between the workpieces to generate heat, melting the metals and joining them. This transformer is highly efficient and fast, and is primarily used in spot/projection welders, seam welders, and butt welders. It is also suitable for difficult-to-weld materials such as aluminum alloys and galvanized steel sheets.
Role Of Resistance welding Transformer?
A transformer in a welding machine adjusts the voltage and current for welding. Standard power sources (110V or 220V) are too high. The transformer steps down the voltage and steps up the current to appropriate levels for effective welding.
How It Works:
1) It uses electromagnetic induction to convert high-voltage, low-current AC power into low-voltage, high-current power.
2) This conversion is achieved by a primary coil and a secondary coil wound around an iron core. The primary coil receives standard power, creating a magnetic field that induces a much higher current in the secondary coil.
3) The secondary coil is connected to the welding electrodes, which generates the heat needed to melt and fuse the metal.
What are the Key components Of A Welding Transformer
1) Iron core: Provides a common magnetic path for the windings, often made of high-efficiency stacking laminated silicon steel thin sheets, is responsible for directing the magnetic flux from the primary to the secondary winding.
2) Primary winding: This is the high-voltage, low-current winding that receives the input power. It consists of many turns of insulated copper wire.
3) Secondary winding: This low-voltage, high-current winding is directly connected to the welding electrodes. It is made of a few turns of very thick copper plate to handle the high welding currents.
4) Cooling system: Due to the high currents and significant heat generated, a robust cooling system often involving water cooling which is crucial for dissipating heat and maintaining the transformer's performance.
Types of welding transformers?
AC, DC, Inverter & portable welding gun
Advantages of using the welding transformer in a welder?
1)Efficiency and Energy Use: The rapid heating process minimizes heat loss, contributing to lower operating costs.
2)Weld Quality and Control: This method produces strong, durable, precise, and repeatable welds. 2) It allows for precise control of heat and pressure. 3) No filler materials are needed, reducing costs and potential impurities. 4) The process generates minimal fumes or sparks, ensuring a cleaner and safer environment.
3)Automation and Productivity: 1) Resistance welding is a high-speed process, suitable for mass production. 2) can be easily automated, increasing productivity and consistent quality while reducing labor costs.
4) Versatility: can join various similar and dissimilar metals, including steel, stainless steel, copper, and aluminum.
Typical issues with welding transformer?
1)Overheating: Caused by short circuits, cooling system failures, or high stress, it can lead to component failure and insulation damage.
2)Insulation failure: Often due to degraded insulation, leading to a short circuit between primary and secondary coils. Condensation can also be a factor.
3)Poor secondary connections: Loose or contaminated connections increase resistance and heat, causing a drop in output.
4)Incorrect selection: Using a transformer with an improper KVA rating, primary voltage, or frequency can result in poor weld quality or transformer damage.
Maintenances and troubleshooting
Regular Maintenance:
1) Clean all components.
2) Check the cooling system.
3) Verify electrical connections.
Troubleshooting:
1) Test the secondary voltage.
2) Inspect for physical damage or contamination.
3) Check all process settings.
4) Observe operator procedures.